Published: 2021-09-30 | 2 min read
- HTML
- JavaScript
- Node.js
- Express
I recently joined a friend on a Node.js and Express project, where I came across some syntax in the name attribute of the input elements that I haven't seen before.
<input
name="spec[testFlows][${flowIndex}][items][${itemIndex}][delete]"
type="checkbox"
/>
<input
name="spec[testFlows][${flowIndex}][items][${itemIndex}][testId]"
value="${item.testId}"
/>
<input
name="spec[testFlows][${flowIndex}][items][${itemIndex}][click]"
type="checkbox"
/>It allowed constructing form inputs into a nested object. I tried searching online and couldn't find any quick explanation of how it worked so I started looking deeper.
I couldn't find anything in the HTML and HTTP request specification and it turns out that this functionality is enabled by Express body-parser middleware,
By default, HTML form data in POST requests is sent in application/x-www-form-urlencoded format, which consists of key and value combinations separated by =, with a & between each pair.
field1=value1&field2=value2body-parser can extract this data by parssing the urlencoded HTTP POST request body, and making it then available on req.body as a JavaScript object inside Express route handlers and other middleware.
Typically, this is used for simple objects where each input field's name attribute corresponds to a property inside the req.body object.
However, it is also possible to construct rich, nested objects using the square bracket notation inside the name attribute of the form input.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));-
express.urlencoded({ extended: true })- this option usesqslibrary, which allows values to be of any type -
express.urlencoded({ extended: false })- this (preferred) option is based on Node's nativequerystringquery parser, which allows values to be strings and arrays
What does it look like in practice?
You can construct the object with square bracket notation, where each property inside the square bracket corresponds with the object property. If the property is as an integer, the value will become part of an array. You can also leave the square bracket empty to avoid specifying the array index and body-parser will determine it based on the order in the form.
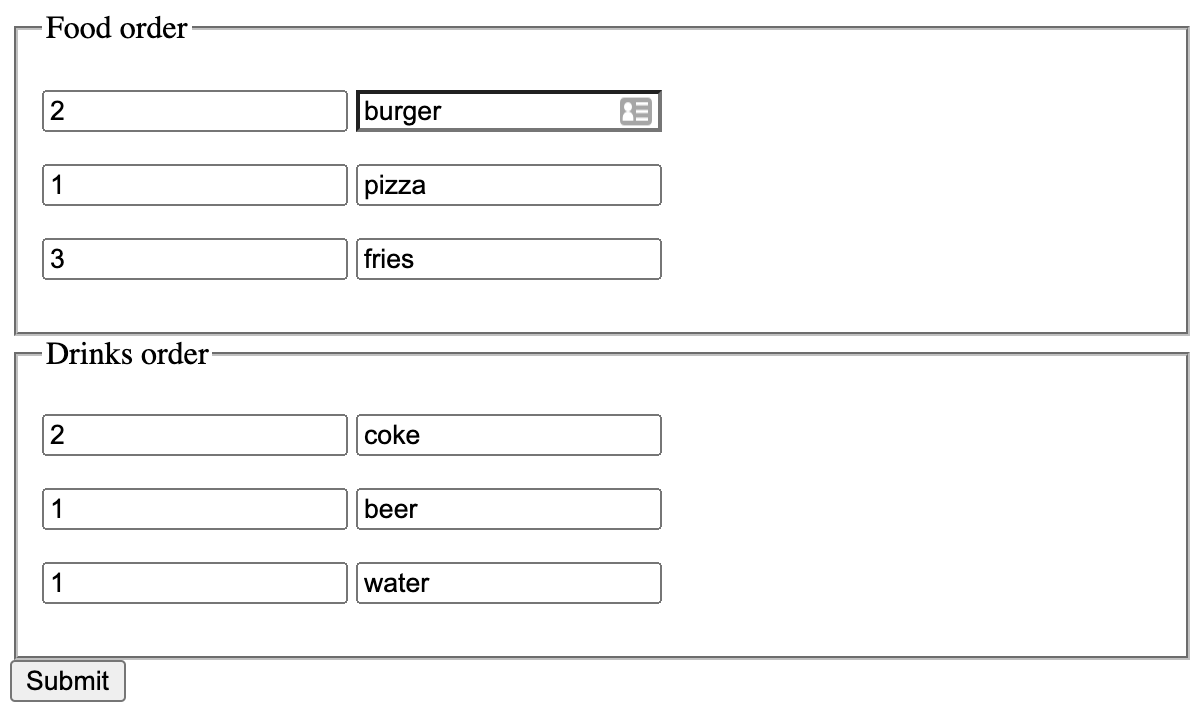
HTML
<form method="POST" action="/order">
<fieldset>
<legend>Food order</legend>
<p>
<input name="order[food][1][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[food][1][meal]" type="text" />
</p>
<p>
<input name="order[food][2][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[food][2][meal]" type="text" />
</p>
<p>
<input name="order[food][3][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[food][3][meal]" type="text" />
</p>
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>Drinks order</legend>
<p>
<input name="order[drinks][1][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[drinks][1][beverage]" type="text" />
</p>
<p>
<input name="order[drinks][2][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[drinks][2][beverage]" type="text" />
</p>
<p>
<input name="order[drinks][3][quantity]" type="number" />
<input name="order[drinks][3][beverage]" type="text" />
</p>
</fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>JavaScript
const express = require('express');
const path = require('path');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.post('/order', (req, res) => {
res.json(req.body);
});
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'index.html'));
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Listening on port ${port}`);
});Form
Output from req.body
{
order: {
food: [
{
quantity: "2",
meal: "burger"
},
{
quantity: "1",
meal: "pizza"
},
{
quantity: "3",
meal: "fries"
}
],
drinks: [
{
quantity: "2",
beverage: "coke"
},
{
quantity: "1",
beverage: "beer"
},
{
quantity: "1",
beverage: "water"
}
]
}
}You can find the code from these examples in this GitHub repository.
Why is this useful?
It allows you to avoid the step of structuring the form data manually into an object on the client or server side, i.e.
- Client
- Managing form inputs in state
- Constructing form data in onSubmit event handler
- Server
- Structuring data in a route handler
Is it possible to use this outside of Express?
You can use body-parser and qs in other Node projects too, since they are available as npm packages.